views
Preparing the Tube
Put on gloves. Wash your hands and put on a pair of disposable medical gloves before advancing with the procedure. Even though you'll have gloves on, you should still wash your hands with warm water and antibacterial soap to further reduce the risk of introducing germs into the nasogastric tube.
Explain the procedure to the patient. Introduce yourself to the patient and explain the procedure. Make sure that you have the patient's consent before continuing. Talking the patient through the procedure before you perform it can allow you to gain his or her trust while also calming the patient down.

Position the patient. For best results, the patient should be positioned in an upright sitting position with his or her chin touching the chest. He or she should also face forward. If the patient has a difficult time holding his or her head up, you may need someone to assist you by holding the patient's head forward. You can also use stiff pillows to hold the head steady. When placing an NG tube in a baby, you can lay the baby back instead of holding him or her in an upright sitting position. The baby's face should be up, and the chin should be slightly raised.

Examine the nostrils. Quickly check both nostrils for signs of deformity or obstruction. You will need to insert the tube into whichever nostril appears clearest. If necessary, use a small flashlight or similar light to look into the nostrils.
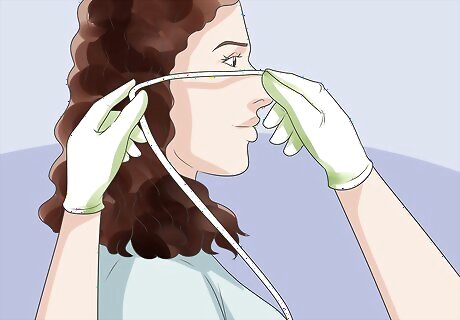
Measure the tube. Measure the necessary tube length by drawing the NG tubing across the outside of the patient's body. Start at the bridge of the nose, then draw the tube across the face to the earlobe. From the earlobe, draw the tube down to the xiphisternum, which lies halfway between the end of the sternum and the navel. This point lies at the center front of the body, where the lower ribs meet. For an infant, this point will be roughly one finger-width beneath the chest bone. For a child, measure two finger-widths. The distance can vary more dramatically for teenagers and adults depending on height. Write down the proper measurement on the tube using permanent marker.
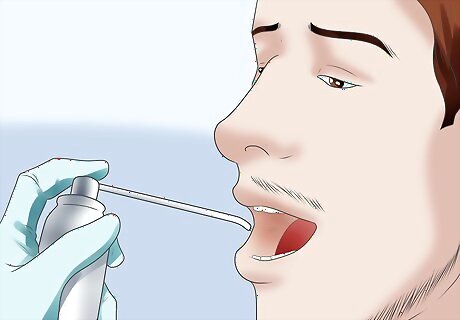
Numb the patient's throat. Spray the back of the patient's throat with anesthetic throat spray. Wait a few seconds for the spray to take effect. This procedure can be uncomfortable for many patients, and the use of throat spray can minimize discomfort and reduce gagging. It is not strictly necessary, however.
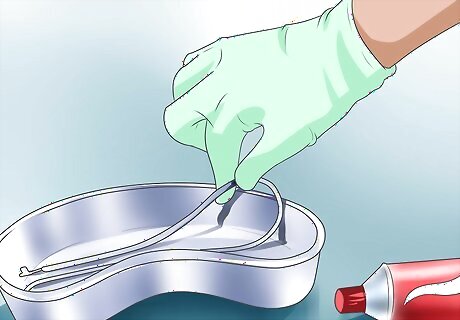
Lubricate the tube. Coat the first 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm) of the NG tube with water-based lubricant. Using a lubricant containing 2-percent Xylocaine or a similar anesthetic can further reduce irritation and discomfort.
Inserting the Tube
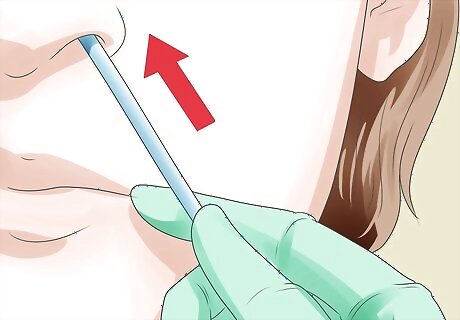
Insert the tube into the chosen nostril. Insert the lubricated end of the tube into the clearest nostril, aiming the end of the tube straight back as you feed it in. The patient must continue looking straight at you. Direct the tube down and toward the ear on that side of the head. Do not allow the tube to feed upward and into the brain. Stop if you feel resistance. Pull the tube out and try the other nostril. Never force the tube inward.
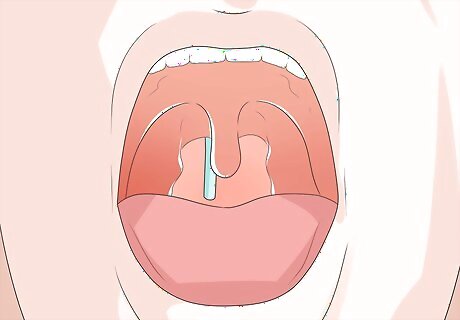
Check the back of the throat. If you have coated the patient's throat with anesthetic throat spray, ask the patient to open his or her mouth and watch for the other end of the tube. For patients who were not treated with throat spray, opening the mouth might be too painful. Instead, you should simply ask the patient to indicate when he or she feels the tube at the back of the throat. As soon as the tube hits the top of the throat, guide the patient's head so that the chin touches the chest. This can help encourage the tube into the esophagus, rather than into the trachea.

Instruct the patient to swallow. Give the patient a glass of water with a straw. Ask him or her to take small sips and swallows as you continue guiding the tube downward. If the patient is unable to drink water for any reason, you should still encourage him or her to dry swallow as you feed the tube into the throat. For infants, give the patient a pacifier to encourage him or her to suck and swallow during the process.
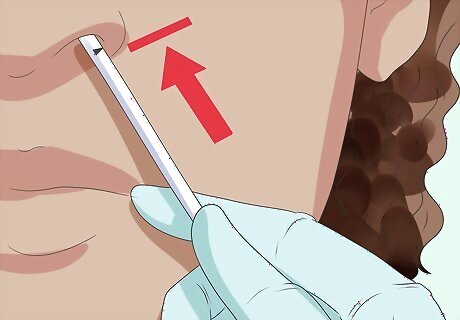
Stop once you reach the measured mark. Continue feeding the tube into the patient's throat until the marked measurement reaches the patient's nostril. If you meet resistance further into the throat, slowly rotate the tube as you advance it. This should help. If the tube still gives considerable resistance, pull it out and try again. Never force it in. Stop immediately and remove the tube if you notice a change in the patient's respiratory status. This can include choking, coughing, or difficulty breathing. A change in respiratory status suggests that the tube has been inserted into the trachea by mistake. You should also remove the tube if it comes out of the patient's mouth.
Checking the Placement of the Tube
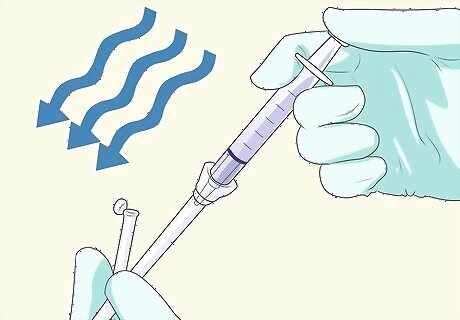
Inject air into the tube. Use a clean, dry syringe to insert air into the NG tube. Listen for the sound it makes using a stethoscope. Draw back the plunger of the syringe to collect 3 ml of air, then attach the syringe to the open end of the tube. Place a stethoscope over the patient's stomach, just below the ribs and toward the left side of the body. Quickly depress the plunger to insert the air into the tube. You should hear a gurgling or popping sound through the stethoscope if the tube has been positioned correctly. Remove the tube if you suspect improper placement.
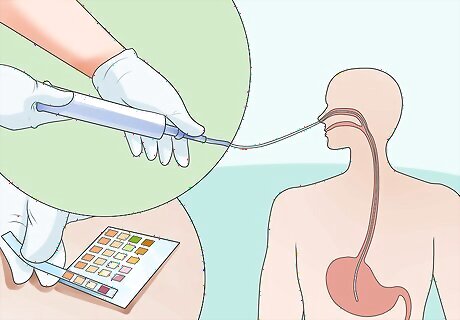
Aspirate from the tube. Use a syringe to draw stomach acid through the tube, then test the contents with pH indicator paper. Attach an empty syringe toe the adapter at the free end of the tube. Lift the plunger to draw 2 ml of stomach contents into the tube. Wet the pH indicator paper with the collected sample and compare the color on the strip to its corresponding color chart. The pH should usually be between 1 and 5.5 Remove the tube if the pH is too high or if you otherwise suspect improper placement.
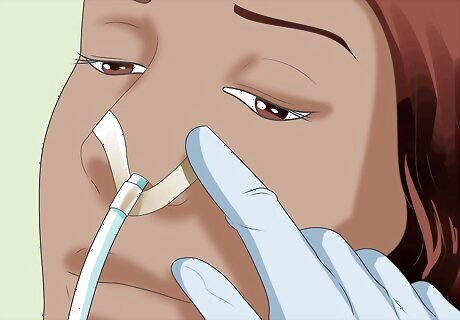
Secure the tube. Secure the placement of the tube by taping it to the patient's skin with 1-inch (2.5-cm) thick medical tape. Attach one piece of tape to the patient's nose, then wrap the ends of that piece around the tube. Place a separate piece of tape across the tube and over the patient's cheek, as well. The tube must not be able to move around as the patient moves his or her head naturally.
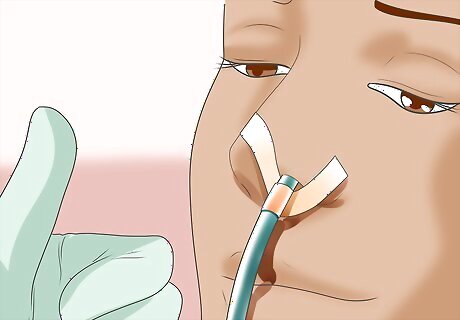
Check the patient's level of comfort. Before leaving the patient, make sure that he or she is as comfortable as possible. Help the patient ease into a comfortable resting position. Make sure that the tube is not cut off or strained. Once the patient is comfortable, you should be able to remove your gloves and wash your hands. Throw the gloves away in a clinical waste bin, and use warm water and antibacterial soap to wash your hands.
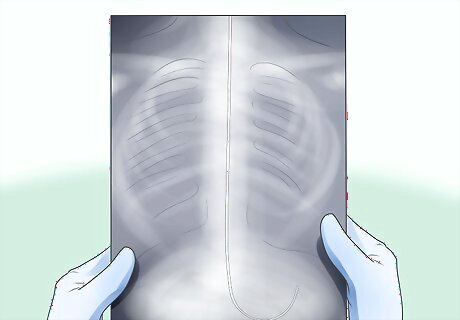
Confirm the placement with an x-ray. If the air test and stomach contents both check out, the tube is likely positioned properly. Nonetheless, it is still a good idea to arrange a chest x-ray to further confirm the placement of the tube. Do this before using the tube to deliver food or medications. The x-ray technician should promptly deliver the x-ray results, and proper placement can then be confirmed by a doctor or nurse.
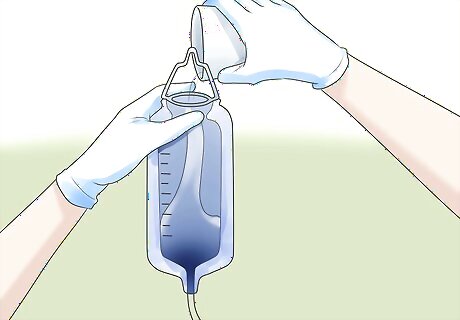
Use the NG tube as needed. At this point, you should be able to use the tube to drain the stomach, insert food, and/or insert medication. You'll need to attach a bile bag to the end of the tube if you want to drain out digestive waste fluids. Alternatively, you may need to attach the end of the tube to a suction machine. Set the machine suction and pressure as indicated for that patient's specific needs. If you need to use the NG tube for feeding or medication, you might need to remove the guide wire from inside before inserting anything into the stomach. Flush 1 to 2 ml of water through the tube before carefully pulling the guide wire straight out. Clean the wire, dry it, and store it in a safe, sterile location for later use. Regardless of what the tube is used for, you should document its usage closely. Write down the reason for its insertion, the type and size of the tube, and all other medical details dealing with the usage of the tube.




















Comments
0 comment