
views
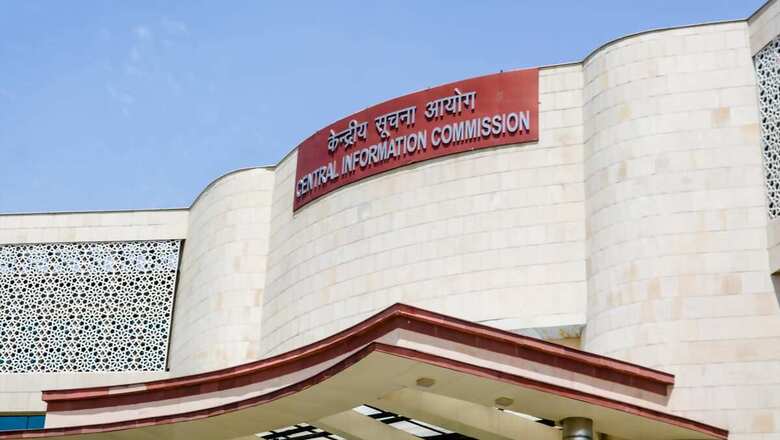
What is Right to information Act 2005?
RTI is an act which sets out the rules and procedures regarding citizens’ right to seek information. Under the Act any citizen of India may request information from a “public authority” which is required to reply expeditiously within thirty days.
What is information?
Information is any material in any form, which includes records, documents, emails, opinions, press releases, orders, reports data material held in any electronic form. It also includes information related to any private body which can be accessed by public authority under any law for the time being in force.
What is the scope of RTI Act?
The Act covers all the constitutional authorities, including Executive, Legislature and Judiciary; any institution or body established or constituted by an act of Parliament or a state legislature. Citizen can inspect any government documents, inspect any government works etc.
What is the procedure to file RTI?
Citizen seeking information are required to send Application to the Public Information Officer (PIO) concerned department along with fee of Rs. 10. If a reply is not received within 30 days, the next step is to approach Central Information Commission (CIC).
Is there any specific format of the Application?
There is no prescribed format of application for seeking information. The application should, however have the name and complete address of applicant along with specifications of the details sought for.
Does the Act provide for partial disclosure?
Yes. Under Section 10 of the RTI Act, access may be provided to that part of the record which does not contain information which is exempted from disclosure under the Act.
Applicant seeking information required to give reasons for seeking information?
The information seeker is not required to give reasons for seeking information.
Can the public information officer (PIO) refuse to give information?
A PIO can refuse information on 11 subjects that are listed in section 8 of the RTI Act. These include information received in confidence from foreign governments, information prejudicial to security, strategic, scientific or economic interests of the country, breach of privilege of legislatures etc.
Is there any organization(s) exempt from providing information under RTI ?
Yes, certain intelligence and security organizations specified in the 2nd schedule of the Act are exempted from providing information except the information pertaining to allegations of corruption and human rights violations.
(The author, Prachi Mishra, is a Supreme Court lawyer and Additional Advocate General, Chhattisgarh)
Read all the Latest News, Breaking News and Coronavirus News here. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Telegram.



















Comments
0 comment