
views
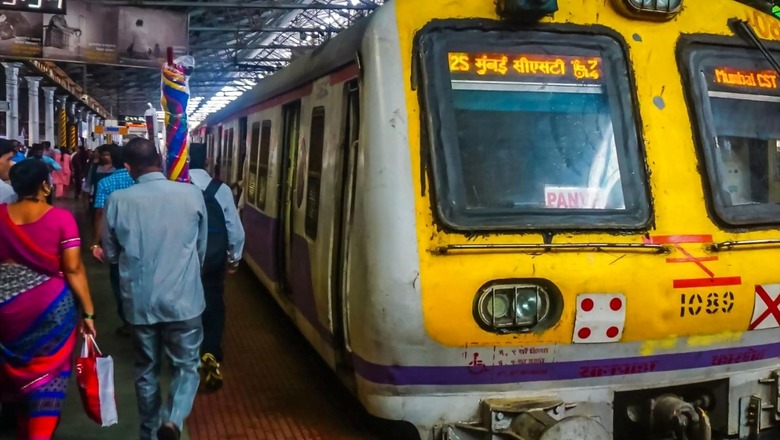
It was the Central Railway (CR) that witnessed the first electric train in India in 1925. Nearly a century later, the Zone has achieved 100% electrification of the Broad Gauge network, an official statement announced on Friday.
The Central Zone has 3,825 route km of Broad Gauge and the last non-electrified section was Ausa Road-Latur Road (52 RKM) of the Solapur Division, was electrified last month, the statement added.
The Central Railway has helped in reducing carbon footprints of 5.204 lakh tonnes every year and also saves Rs 1,670 crore annually, it added.
“Indian Railway is working in mission mode to become the largest Green Railway in the world and is moving towards becoming a ‘net zero carbon emitter’ before 2030…The pace of Railway Electrification, which is environment friendly and reduces pollution, has increased at 9X speed since 2014,” they said.
The Railways has planned electrification of Broad Gauge routes, which will facilitate elimination of diesel traction resulting in significant reduction in its carbon footprint and environmental pollution.
It was the CR where the first electric train ran in India between the then Bombay Victoria Terminus (now Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Terminus) and Kurla on Harbour line on February 3, 1925.
“The section was electrified in 1,500 Volt DC. The conversion of DC traction on Mumbai Division of Central Railway to AC traction began in 2001 and progressively, without significant disturbance to the lifeline of the nation, i.e. suburban services, was completed in 2016,” it said.
It has overcome the challenges of conversion of DC-AC traction and ghat sections over the years.
The Central Railway is strategically located at the middle part of India and connects most of the Indian cities and other locations with the major cities in its jurisdiction like Mumbai, Nagpur, Pune, Nasik, Solapur, and Kolhapur.
The Punjab Mail Express, Howrah Mail, CSMT-H.Nizamuddin Rajdhani Exp, Deccan Queen, Vande Bharat, Tejas Express, Konkan Kanya Exp, Pushpak Express, Mahanagari Express, Udyan Express, Shatabdi Express, Hussain Sagar Express, and Siddeshwar Express are among the major prestigious trains that are running over Central Railway network.
In the statement, Naresh Lalwani, General Manager, Central Railway, said: “Railway is guided by a historical vision of being an environment friendly, efficient, cost effective, punctual and a modern carrier of passengers as well as the freight in order to serve the growing needs of New India. This will also significantly reduce the fuel bill and earn carbon footprints.”
Electrification offers a number of advantages, including reduction in dependence on imported diesel fuel, thereby saving precious foreign currency and reduced carbon footprints and reduction in operating cost.
In June 2021, the West Central Railway (WCR) became the first zone of the railways that achieved 100 percent electrification.
So far, a total of seven railway zones out of 18 have been electrified, latest being the Central and the North Eastern Railways. Other zones that were electrified are: East Coast Railway, North Central Railway, Eastern Railway and South Eastern Railway.
Read all the Latest India News here


















Comments
0 comment