
views
- For slow internet, move your router so there are as few obstacles as possible between it and your device.
- Restart your router and modem to resolve common internet connection issues.
- If your problem persists, try updating your router firmware by navigating to its router login page.
Slow or Inconsistent Wi-Fi Connections

Move closer to the wireless router. Sometimes your computer or smartphone is too far away from the checkpoint to connect to Wi-Fi. Move closer to your router and try to connect again.
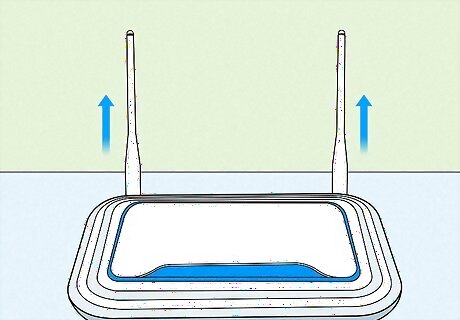
Position your router antennas upward. If your router has antennas, repositioning them can help create a better signal. Wi-Fi signals mainly emit horizontally out of the sides of the antennas. Position them so that they’re vertical, at a right angle to the ground. If you’re having connection issues on a different floor of your home, try different antenna angles for better coverage.
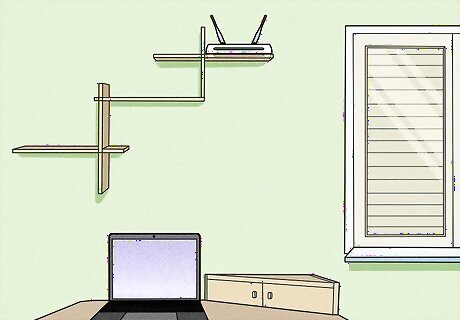
Make sure that you have a clear line-of-sight between your device and the router. If you can't draw a line from your Internet-connected item to the router without passing through walls, appliances, furniture, or the like, your chances of maintaining a good Internet connection deteriorate. The best way to ensure a consistent Internet connection is by minimizing the number of obstacles between your Internet device and the router.

Try a Wi-Fi extender. Wi-Fi extenders are devices that wirelessly connect to your router and duplicate its signal, increasing its range. This is helpful if the device you want to connect to the internet is far away from the router.
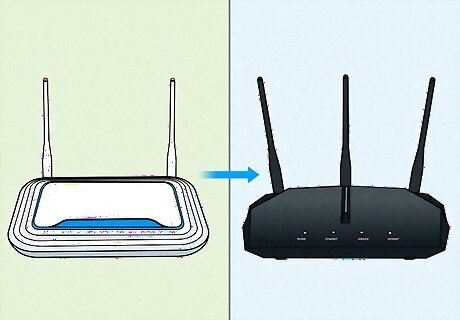
Upgrade your router. Routers with antennas have better range and connectivity, which could resolve slow or inconsistent connections. Make sure to check what speed your router is rated for. This is typically labeled AC####, where the four numbers represent the speed in megabits per second (mbps). Get a router that matches or exceeds your internet plan’s mbps.
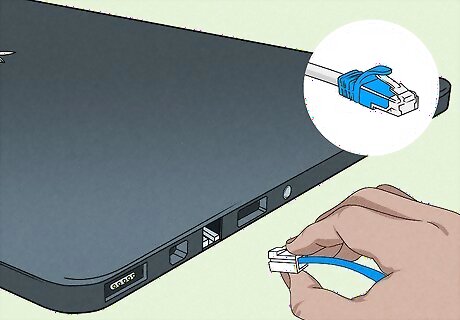
Try using Ethernet. Connecting your computer or console to your router or modem via an Ethernet cable will both speed up your Internet when it's working and help determine whether the issue is with your Internet or your equipment. If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the router, your computer's wireless reception is most likely the problem. If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the modem, then the issue is likely cause by your router. If you cannot connect to the internet while connected directly to your modem, there is something wrong with the modem or with your internet service in general. You'll need to get in touch with your internet service provider's technical support line to fix modem-related issues.
Simple Fixes for Connection Issues
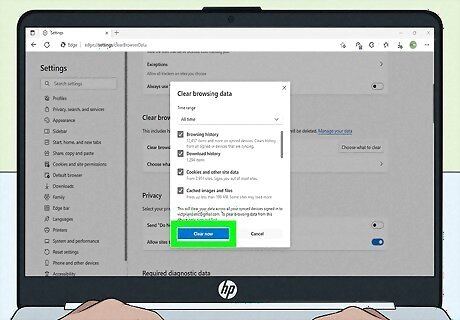
Clear your browser's cache. Much like the DNS cache, your browser's cache makes loading previously visited sites faster, but it can also result in errors if the cache database becomes outdated. To stay relatively up-to-date, consider clearing your browser's cache once per month.

Try a different website or program. There's always a chance that the website you are trying to visit is currently down, or the program you are using is having server problems on its end. Try another website or online program to see if you can connect. Try another web browser if possible as well. For example, you may be having a problem with Chrome, whereas Firefox works fine. If just one of your web browsers is at fault, see the articles below for instructions on repairing it: Chrome Firefox Internet Explorer

Restart your computer. This may seem like a pointless suggestion, but restarting your computer is often the easiest way to fix a vast majority of the issues you may be having. A simple reset will clear out bad settings which could be causing your connectivity issues, and if it doesn't help, it only took a minute! Restarting your computer will often also turn back on your Internet adapter if it was off.

Ensure that your laptop's wireless adapter is enabled. Many laptops have a switch or button that turns the wireless adapter on and off. If you've accidentally pressed the button, your computer will disconnect from the network. Press the button or toggle the switch to turn your wireless adapter back on. You may have to hold the Fn button in order to be able to press the Wi-Fi button. The Wi-Fi button usually looks like three curved lines increasing in size. Skip this step on a desktop computer.

Restart your modem and router. The easiest way to do this is by unplugging both your modem and your router from their respective power sources, waiting for a few seconds, and plugging them back in. Like restarting your computer, this can solve the bulk of minor Internet issues.
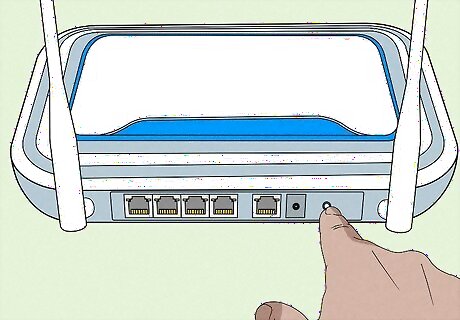
Perform a soft reset on your network. A soft reset causes your router and modem to clear their respective caches and refresh. You can usually perform a soft reset by pressing a power button on the front or side of your router. Many modems can also be soft-reset in this manner. In some cases, you can soft-reset your network by opening your router's page and clicking a Reset button in the "Advanced" or "Power" options.
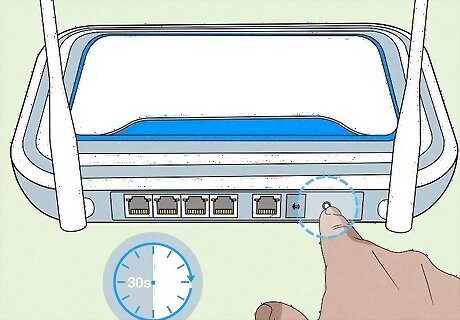
Perform a hard reset on your network. A hard reset causes your router and modem to forget all of your settings, restoring the network to its factory settings (including the factory network name and password). To perform a hard reset, press and hold the "reset" button on the back of the modem for around 30 seconds, allow the modem to reboot, and perform the same step on the router. In most cases, the "reset" button is a recessed button on the back of the modem and router, meaning that you'll need to use a pen or a paperclip (or similar tool) to press the button.
Advanced Fixes for Connection Issues

Update your router. Your router should typically update automatically, but some models may need to be updated manually. You can typically update the firmware by going to the router’s login page in your web browser. Check the manual for the URL. Follow our complete guide to updating router firmware by clicking this link.
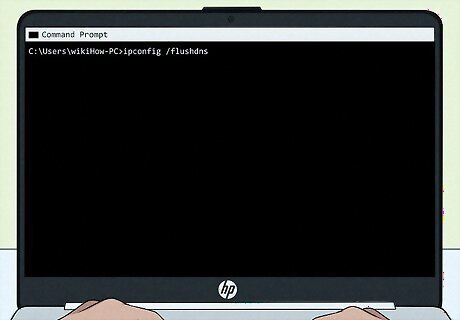
Clear your computer's DNS cache. The DNS cache is responsible for recording website addresses as you access websites, which makes accessing those same websites later a faster process; however, as websites update their addresses, the DNS cache can become outdated, which causes errors. Clearing the DNS cache will resolve issues such as websites failing to load, especially if you can view the website in one browser but not another. To clear the DNS cache on a mobile item such as a smartphone or a tablet, simply restart the item.
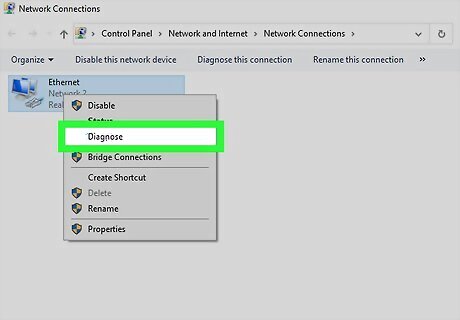
Repair your connection. There could be a software problem on your computer causing the connectivity problem. Both Windows and Mac computers have built-in repair tools that you can use to try to fix the issue: Windows - Press ⊞ Win+R > type in ncpa.cpl > click OK > right-click your network adapter > click Diagnose > follow any on-screen prompts. Mac - Click the Apple menu Mac Apple > click System Preferences... > click Network > click Assist Me... > click Diagnostics > follow the on-screen prompts.

Boost your Wi-Fi signal. If the problems you're experiencing are signal-related, it usually means that interference and distance are the main cause. There are several things you can do to help minimize interference and increase your network's range: Add a second router to extend the range. Increase your computer's Wi-Fi reception. Make your own directional "cantenna" for your wireless adapter.
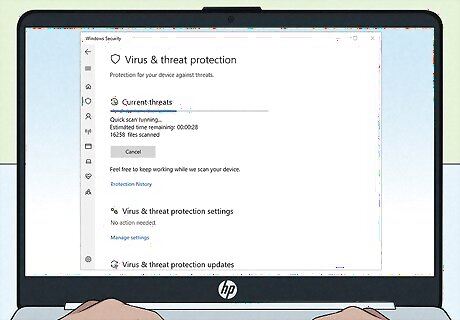
Perform virus and malware scans. Viruses and other malicious computer infections may be hindering your ability to get online. You can usually eliminate viruses by using your computer's antivirus protection.

Contact your internet service provider. If all else fails, this is the best remaining course of action. Explain to your ISP the specific issues you are experiencing, and request someone to come and investigate the problem. Remember to be as calm and polite as possible, and do not take out your frustration on the company.




















Comments
0 comment