views
X
Research source
Don’t worry, we’ve put together a guide to help you get a tick head out, prevent infection, and know when to seek care.This article is based on an interview with our board certified veterinarian, Natalie Punt, founder and CEO of mPet. Check out the full interview here.
Removing an Embedded Tick Head
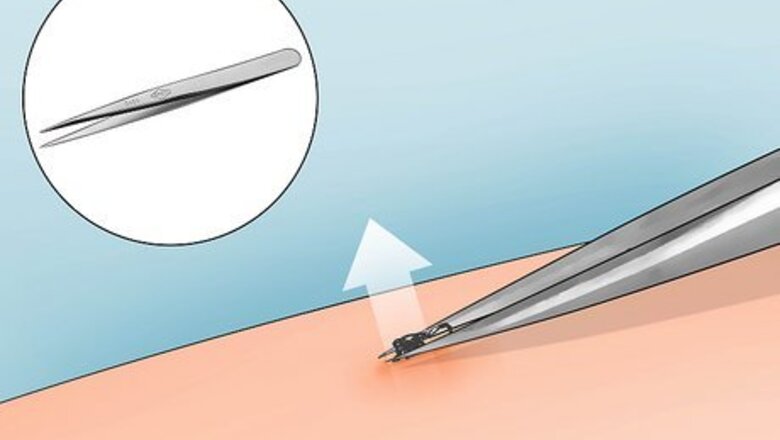
Try to remove the head with tweezers or a sterilized needle. Firmly grasp the head and pull it straight out without twisting. Use even pressure as you pull. Don’t handle the tick with bare hands or try to use a hot match to get the tick out. If the body is still attached, grasp the tick’s body as close to the skin as possible. That’ll give you the best chance of getting the head out, too. If the head breaks apart into tiny pieces as you remove it, don’t try and dig around, or you might cause infection. Sterilize your tweezers with isopropyl alcohol both before and after you pull the tick out. To transmit disease, a tick usually needs to be embedded for 36 hours.
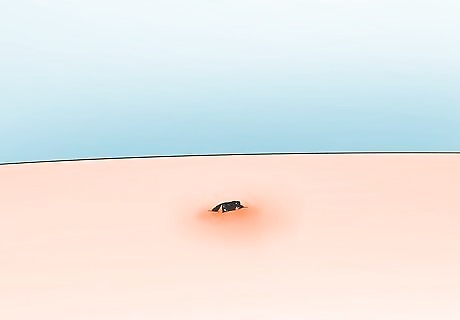
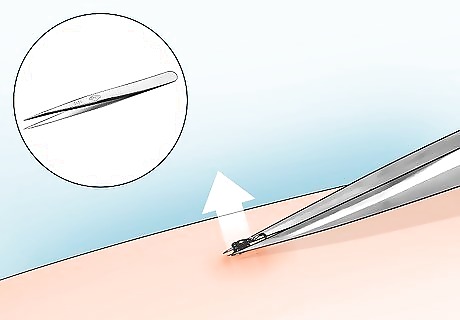
Leave the head alone if you can’t fully remove it. It might seem a little gross, but your skin will heal and shed the head like a splinter. The head should come out in a few days, and in the meantime, follow the steps in the next method to prevent an infection. Soak the skin in warm water to help expel the head faster.
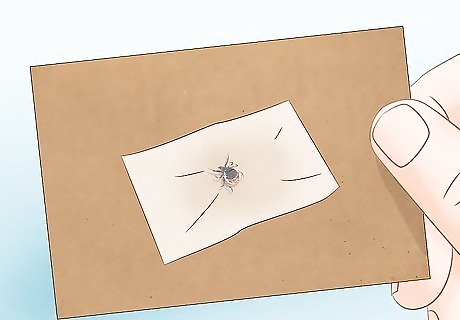
Wrap the tick body in tape, a sealed bag, or a container. After you'll pulled the tick out, it’s helpful for your doctor to see the tick if you develop any potential symptoms. As you seal the tick up, be careful not to squeeze the tick with your fingers, since that can increase your risk of coming into contact with disease-causing bacteria. If you just have a tick head, dispose of the head safely by putting it in alcohol or flushing it down the toilet.
Caring for the Tick Bite Site
Wash your hands with soap and water. Whether you removed the tick from your own skin or someone else’s, it’s crucial to clean off your hands. Washing your hands can protect you from tick-borne disease. Scrub your hands for at least 20 seconds. If you don’t have access to soap and water, use alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
Clean the bite area with soap and water or rubbing alcohol. Washing the area thoroughly with soap and water reduces your chance of infection (both from the tick and from contact with tweezers or your hands). Cleaning the bite area is also a safe wound care step for pets. Just use a non-toxic soap designed for pets. You shouldn’t use shampoo designed for humans, because our skin has a different pH.
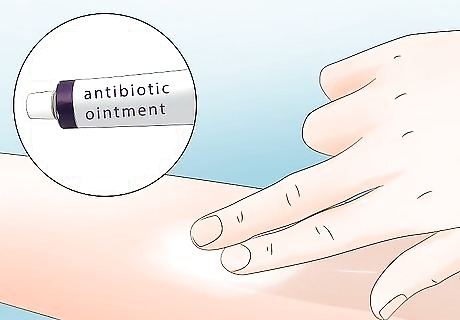
Apply antibiotic ointment. Prevent infection and soothe the skin by applying polysporin or your preferred over-the-counter antibiotic cream. You only have to apply the ointment once. Pets may have an allergic reaction to over-the-counter antibiotic ointment for humans. Apply a small amount first to test your pet’s tolerance. As long as they don’t develop a rash or hives, it’s safe to use. If you decide to use polysporin on your dog, you should also cover the tick bite or put your pet in a cone to prevent them from ingesting the ointment.
Monitoring for Tick-Borne Disease
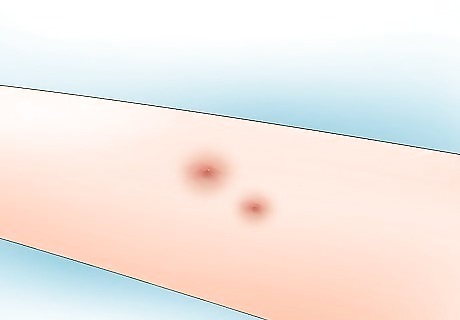
Expect to see a small, tender bump for a few days. It might look like a pimple, but you shouldn’t be worried about this mild reaction. This is just your skin’s response to minor irritation. It’s not a problem unless the bump starts to get significantly larger or redder.
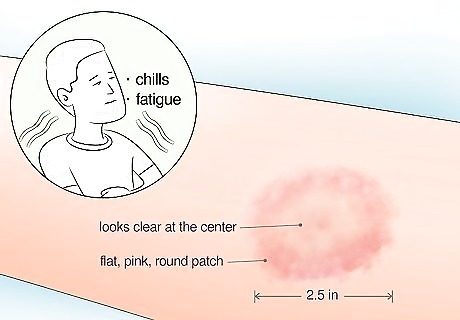
Look out for symptoms of Lyme disease or serious infection. Keep an eye on the bite area for several weeks after you remove the tick. Lyme disease will typically show up in 3-10 days after the bite, but it could take up to 30 days for you to spot symptoms. A flat, pink, round patch and/or fever could signal Lyme disease. The patch might look clear at the center and it can grow to 2.5 inches (6.4 cm) across. Look out for these symptoms of infection, too: Chills Fatigue Redness, soreness, or swelling at the bite site

Don’t send the tick in for testing. You might wonder if you should send the tick to a lab to test if it’s carrying a disease. However, the CDC doesn’t recommend lab-testing ticks. The lab might not give you a good reading, because even if the tick tests positive, you might not have actually been exposed. Plus, symptoms of a disease will often show up before you get results back. You can, however, bring the tick to a vet or doctor for visual identification. They can give you information based on your region and the type of tick to help you figure out if you’re at risk for Lyme disease.

















Comments
0 comment