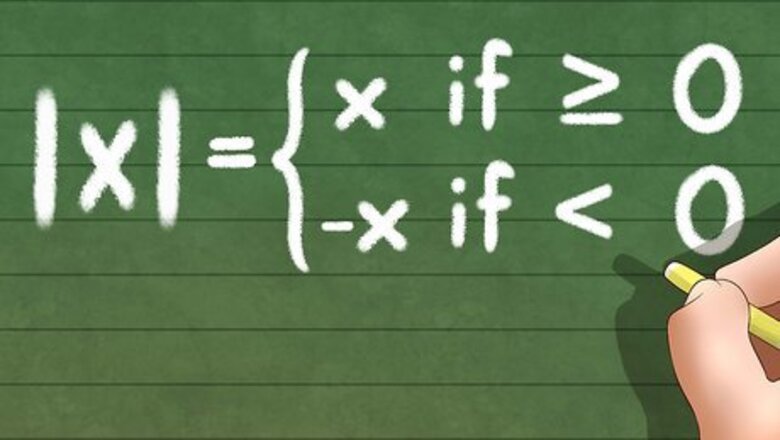
views
X
Research source
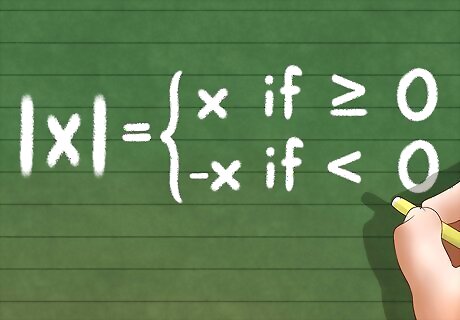
Evaluate the form of the absolute value inequality. As mentioned above, the absolute value of x, denoted by │????│, is defined as: Absolute value inequalities usually take one of the following forms:│????│< or │????│>???? ; │????±????│???? ; │????????2 +????????│a , where ????(????) is any function, and a is a constant.
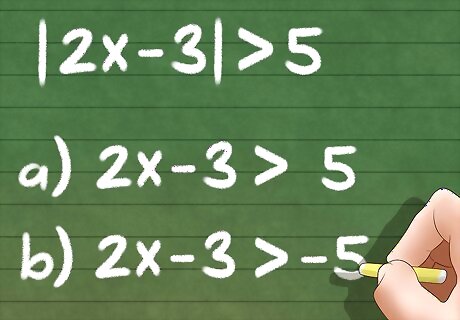
Transform an absolute value inequality into normal inequalities. Remember that an absolute value of x can either be positive x or negative x. The absolute value inequality │????│< 3 can also be transformed into two inequalities: -x < 3 or x < 3. For example,│x−3│>5 can be transformed into – (????−3)>5 or ????−3>5.│3????+2│ <5 can be transformed into – (3????+2)<5 or 3????+2<5. The term “or” means that either of the two will satisfy the given absolute value problem.
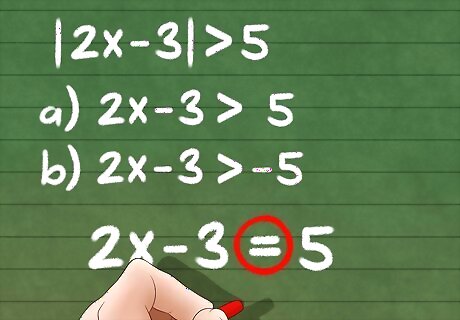
Ignore the inequality sign while you solve for x for the first equation. If it helps, temporarily replace the inequality sign with an equal sign until the end.
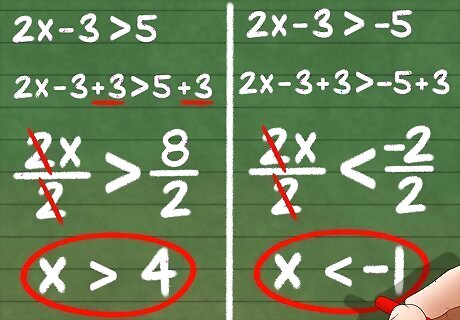
Solve as you would normally for x. Remember that if you divide by a negative number to isolate x on one side of the inequality sign, you will also have to switch the inequality sign. For example, if you divide both sides by -1, -x>5 will become x<-5.
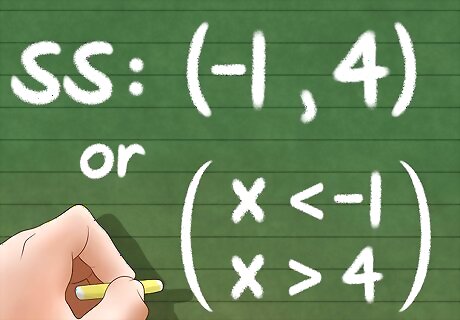
Write the solution set. From the values above, you need to write the range of values that can be substituted in for x. This range of values is often referred to as a solution set. Since you would have to solve two inequalities from the absolute value inequality, you will then have two solutions. In the example used above, the solution can be written in two ways:
-7/3 Check your work. Pick a number within your solution set, and plug it in for x. If it works, great! If not, go back and check your arithmetic.




















Comments
0 comment