
views
- Kimberlite is a volcanic rock containing isolated pieces of rock or crystal that were pushed up out of the earth’s mantle by magma.
- Kimberlite can be identified by its fine-grain texture, its blue or yellow color, and/or the presence of diamonds and other gems in the rock.
- To confirm that you’ve found kimberlite, send a sample to a local geological company or university for a thin section and geochemical analysis.
Identifying Kimberlite

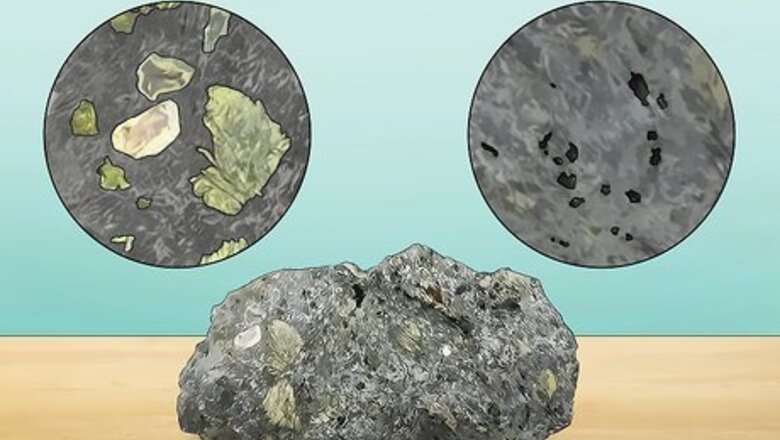
Look at the texture of the rock. Kimberlite has a fine-grained texture and can look glassy or crystalline. In kimberlite deposits, you might see small or large chunks of mantle rocks, minerals, and other foreign rocks or crystals (called xenoliths). It also has high porosity, which means it contains a lot of small voids or spaces that can be seen under a microscope. If the kimberlite is in a sill or dike (a horizontal or vertical rock that cuts through another rock), it tends to have no definable form, but if it’s found in carrot-shaped pipes, it’s often brecciated or fragmented.

Examine the mineral composition of the rock. Kimberlite is primarily made out of olivine and carbonate minerals, with trace amounts of magnesian ilmenite, chromium pyrope, chromium diopside, and other minerals. Kimberlite contains chunks of crystals and other minerals that range in size from 0.5 mm to 7.87 inches (19.98 cm)—which means the mineral composition is slightly different for each deposit. Most kimberlites contain a mixture of mineral chunks of olivine, forsterite, garnet (almandine-pyrope), magnetite, zircon, phlogopite, chromium diopside, and in rare cases, diamonds. Kimberlite used to be divided into two groups based on their mineral composition. However, group II (called kimberlite or orangeite) is now identified as olivine lamproites, which is different from kimberlite.

Observe the color of the rock. Kimberlite that hasn’t been eroded, decomposed, or oxidized is commonly called “blue ground” because of its slate blue, purple, dark blue-green, greenish, brown, or dark gray to black color. “Yellow ground” kimberlite has been weathered away and appears more yellow than blue, purple, brown, or green. Altered kimberlite is more yellowish because the magnetite in the rock has oxidized to limonite.

Send a thin section to a local university or science lab. If you’ve collected a sample of rock and want to confirm that it is kimberlite, you can send it to a local geological company or university (like Colorado School of Mines or the University of South Florida) and have them do a thin section and geochemical analysis. Both of these tests can cost around $200 to $400 total.

Contact a geologist to try and conduct a survey. Kimberlite contains magnetite, which means that it can be magnetic. Geologists can find kimberlite by flying above the ground in planes and measuring the magnetic properties of the rock layers underground with specialized equipment. Ask the National Society of Professional Surveyors, the American Institute of Professional Geologists, or your local state geological survey if you need expertise or testing from professionals in your area. Geologists might also use hyperspectral imaging and sound waves to create a map that they can compare to signatures of certain rocks, like kimberlite, that contain valuable minerals.
Locating Kimberlite
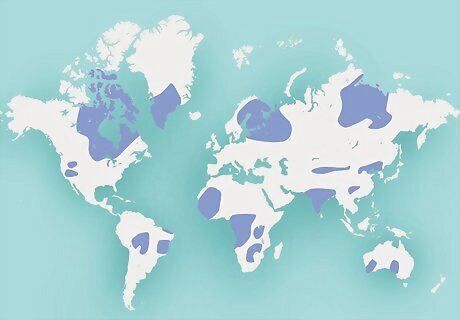
Kimberlite is found in ancient areas of the earth’s crust. Some kimberlites might be found outside of these old continental cratons (like Kentucky, Wyoming, Colorado, Kansas, or Arkansas in the US). However, they’re mainly found in countries where the rocks are old, like South Africa, Russia, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Brazil, China, Canada, Botswana, Zimbabwe, Angola, and Australia. In South Africa, a palm-like tree called Pandanus candelabrum appears to prefer growing on soil above kimberlite. Seeing this shrubby tree might indicate that the rock below it is kimberlite. Some kimberlite can be found near or at the earth’s surface, while some may be underground and require mining or drilling to access.
What is kimberlite?

Kimberlite is a volcanic rock that contains crystals and minerals. Kimberlite is officially classified as a “potassic ultramafic rock with inequigranular texture,” which means it’s an igneous (lava or magma) rock that is low in silica and contains potassium, magnesium, and iron. It also contains isolated chunks of rock or crystal that were formed in a different place than the kimberlite. Diamonds and other minerals don’t grow in kimberlite—instead, kimberlite eruptions pushed these minerals further to the surface, saving diamonds from transforming into graphite.
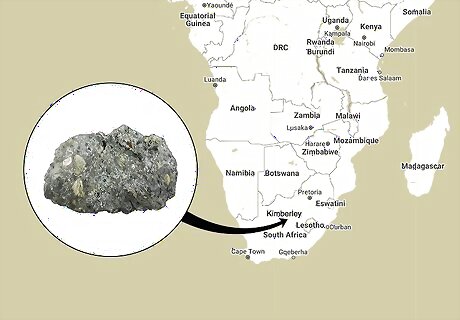
Kimberlite was named after Kimberley, South Africa, where it was discovered. In 1887, an American geologist named Henry Carvill Lewis named and described kimberlite as a brecciated (broken into angular fragments) peridotite (dense coarse rock that contains a large amount of olivine). In 1867, a local farmer’s discovery of diamonds that had eroded out of kimberlite and went into the Orange River caused South Africa’s first diamond rush and led to the creation of diamond mines.

Kimberlite is classified into three types based on its characteristics and location. Kimberlite is formed by magma eruptions from deep within the earth’s mantle. Although the exact process of how kimberlite magma rises or forms is still not understood by scientists, geologists have identified three main facies: Crater kimberlite: Found within a volcanic crater, this type of kimberlite is a breccia or fragmented rock that contains country rock, crystals, and volcanic ash. Diatreme kimberlite: This kind creates a deep cylindrical or funnel-shaped pipe in the earth called a diatreme, and is made up of fragmented country rock and volcanic debris. Hypabyssal kimberlite: This kimberlite is found near the surface of the earth and is less fragmented than the other two types. It has a porphyritic texture, which means it has large crystals surrounded by smaller crystals.
Kimberlite and Diamonds

Kimberlite is one of the main rocks in which diamonds can be found. Diamonds form at least 100 miles (160 km) below the surface of the earth, in the upper mantle. The diamonds at the surface of the earth were transported quickly upwards by violent magma eruptions millions of years ago. They’re found in weathered and unweathered kimberlites and lamproites. These kimberlite eruptions happened very quickly because otherwise, the diamonds would have turned into graphite. Scientists predict the kimberlite pipes may have traveled around 20 to 30 mph (32 to 48 km/h).
Differentiating Kimberlite From Lamproite

Kimberlite and lamproite have different minerals, formations, and shapes. Although they’re both igneous rocks rich in potassium and magnesium, they have several important differences. Here are the most important differences between the two magma rocks: While lamproites are more common, we only know of about 4 or 5 lamproite formations that contain diamonds, compared to the 900 diamondiferous kimberlite pipes we know of. Kimberlites don’t contain silica, while lamproites do. Kimberlite pipes go deep into the earth and might no longer have lava flow, while lamproites might have lava flow.
How do kimberlite pipes form?

Kimberlite pipes are relatively rare geological formations. Although scientists aren’t sure how the magma pipes travel, they know the general process. This is how kimberlite pipes have formed over millions of years: Molten rock from the mantle moves upward towards the surface of the earth at a high rate of speed. As the magma rises, it traps a variety of minerals and rocks from the mantle, including diamonds. The magma comes into contact with the cool Earth’s crust and slows down, solidifying into a volcanic pipe formation. The violent explosive eruption causes the volcanic pipe to expand quickly, creating a large, carrot-shaped formation in the earth called a kimberlite pipe. The weathering and erosion of kimberlite pipes over time expose them to the surface of the Earth, making them accessible for mining and exploration.

















Comments
0 comment