views
Treating Your Cyst at Home
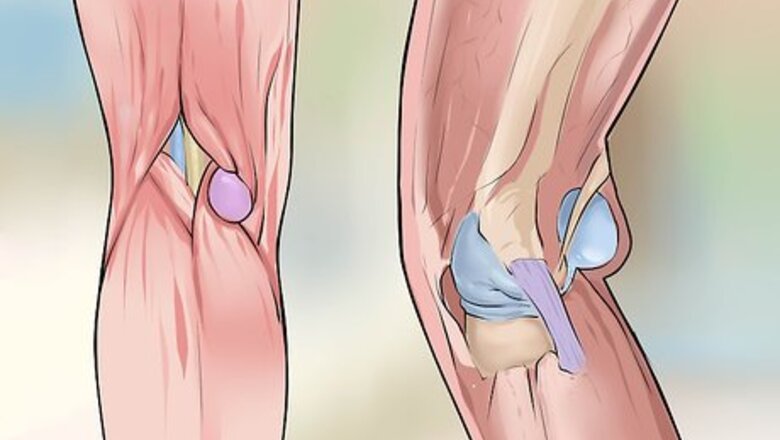
Know the difference between a Baker's cyst and something more serious. Though you may be able to treat your Baker's cyst at home, you want to make sure it is, in fact, a Baker's cyst and not something that requires medical attention, such as deep vein thrombosis or arterial obstruction. If you experience swelling or purplish marks on your toes and feet, see a doctor right away.

Rest your affected knee. Rest your knee until it no longer hurts to put pressure on it. Note any pain you specifically feel around or behind your knee while flexing and extending your leg. You should rest your knee as often as possible for at least a day or two.
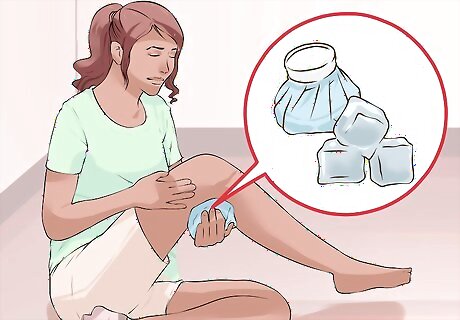
Ice your knee around the cyst. Ice your knee injury as soon as possible. Icing helps reduce swelling and inflammation around the injury, which will also help relieve some of the pain. Only leave the ice on your knee for 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Allow the area to warm to room temperature (another 15 to 20 minutes) before reapplying the ice. This can help reduce swelling and pain for the first day or two after the initial injury, and you can ice your knee as often as you want during this period. Wrap a bag of ice (or something frozen, like a bag of peas) with a towel (never directly to the skin) before you apply it.
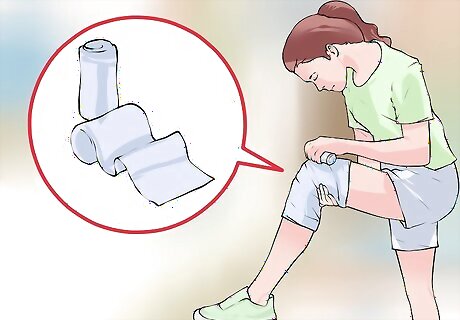
Use a compress. A compress helps reduce swelling to the injured area, and it also helps to stabilize your knee. Tie an elastic bandage (ace wrap), trainer's tape, a brace, or even a piece of clothing around the injury. Tie it tightly enough to stabilize your knee but not so tightly that you cut off circulation.
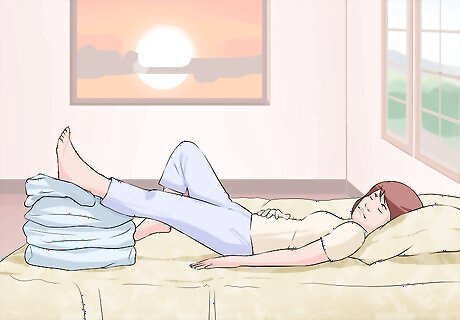
Elevate your leg. Elevating your leg also helps reduce swelling, and it returns blood to the heart. While lying down, raise your leg above the level of your heart (or as high as you can without causing pain). If you can't raise the injured leg, try to keep it at least parallel to the ground. Also try placing pillows under your legs when sleeping to keep them elevated.
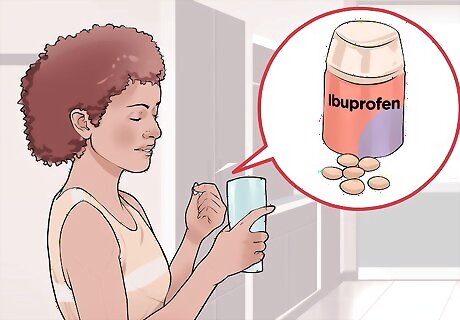
Take an over-the-counter (OTC) pain medication. You can take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, aspirin, and naproxen, to help reduce pain and swelling. Follow the dosage on the label and stay within the recommended daily allowance. Take medications with meals and water. Aspirin should not be given to children or adolescents under 19 due to the possibility of Reye syndrome (brain and liver damage), especially if the child has chickenpox or the flu. Talk to your doctor before giving aspirin to your child. Medical professionals recommend consulting your doctor before taking NSAIDs if you have liver, kidney, or stomach issues.
Seeing Your Physician
Have your doctor evaluate the injury. Have your doctor investigate and treat the underlying cause of the cyst. Causes can include knee trauma, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and cartilage or tendon trauma to name a few. Allow your doctor to examine you so they can make a proper diagnosis.

Go back for a check-up if your cyst gets bigger. An enlarged cyst could cause swelling in your lower leg because it might compress the nearby veins. Because of this, it's important to see your doctor if your cyst grows. Allow your doctor to examine you, then follow their treatment advice. When you call to make the appointment, tell the doctor's office that you're concerned that your cyst is growing.
Consult your doctor if the cyst ruptures. Even if you've already consulted your doctor for a treatment plan, return if you suspect the cyst has ruptured or encountered other complications. If your Baker's cyst ruptures, the fluid will leak into the calf area in your leg, which can lead to: The sensation of water running down your calf Redness and swelling Bruising that spreads from the back of your knee to your ankle Sharp pain due to the leaked fluid and subsequent inflammation, which can lead to blood clots. Since these symptoms can resemble those of a blood clot, see a doctor immediately in the event that you need to be treated for a clot. Dislodged blood clots can lead to life-threatening conditions. If your doctor determines that you're not at risk for complications due to the rupture, then your leg will reabsorb the fluid in anywhere from 1 to 4 weeks, and your doctor will recommend or prescribe a pain medication.

Ask your doctor about steroid injections. A clinical study has shown that swelling, pain, and range of motion all improve after direct injection of corticosteroids into the cyst for patients who suffer from osteoarthritis-induced Baker's cysts. Your physician will inject a needle with corticosteroids directly into the cyst cavity. The steroids help reduce the inflammation and swelling at the site. Your doctor may also use an ultrasound machine to visualize the cyst and help guide the needle.

Ask your doctor about draining the cyst. Your doctor may also remove the fluid within the cyst itself. If you have secondary cysts (fluid accumulation from the front and back of the knee), your doctor may also remove fluid from the front or side of the knee as well. This will allow greater comfort by reducing pain and swelling and allowing you to move your knee more freely. Your doctor will use an ultrasound to correctly inject a needle into the fluid and will pull back on the plunger to suck it out. Your doctor will use an 18 or 20-gauge needle due to the thick fluid within the cyst(s). Your doctor may also need to perform the procedure more than once depending on the amount of fluid present or because the fluid has accumulated at multiple sites. It’s common for doctors to perform both an aspiration (drainage) followed by a steroid injection. Multiple studies have shown a reduction of symptoms and better function of the knee after both procedures.
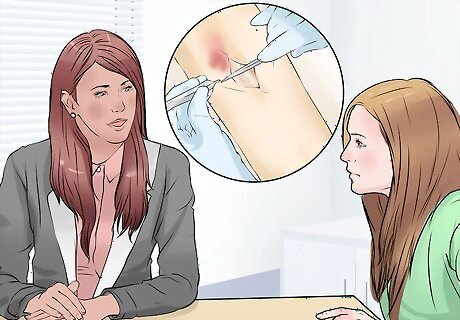
Discuss surgical excision of the cyst. This is a last resort if symptoms persist, other treatments have failed, or the cyst has become very large. While you are under anesthesia, your surgeon will make small (3 to 4-millimeter) incisions around the cyst to drain the fluid. The surgeon may not remove the entire cyst because it can typically resolve on its own. The surgeon will stitch the incisions once the cyst has been drained. The procedure typically takes an hour or less based on the size of the cyst. A larger cyst will take longer because the swelling may have wrapped it around nerves and blood vessels. You can expect to be given pain medication as needed. Once home, follow the RICE therapy method (rest, ice, compression, and elevation). Your surgeon may suggest crutches or a cane to keep weight off the area for several days.
Maintaining Joint and Muscle Strength with a Baker's Cyst

See a physical therapist. Inflammation to the area of a Baker's cyst can cause muscle tightness and joint stiffness. Perform pain-free flexibility and strengthening exercises to help rehabilitate the area and keep joints and muscles active. This will help prevent future weakness and/or stiffening of the surrounding muscles and joints. Focus on your quadriceps, hamstrings, buttocks, and calf muscles.
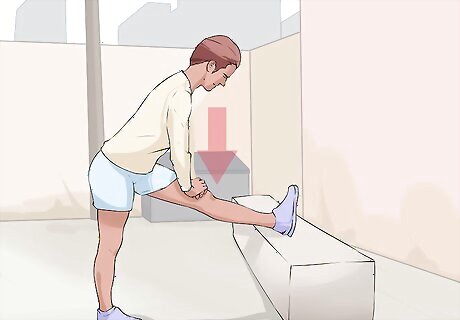
Perform standing hamstring stretches for flexibility. Find a stool or object that is about 1.5 feet (50 cm) high. Rest the foot of your uninjured leg on the stool with your knee slightly bent. Lean forward and down—keeping your back straight—until you feel a stretch in your thigh. Hold the position for thirty seconds. Perform 3 repetitions twice daily, as well as before and after exercising. If you do not feel much of a stretch, try leaning slightly to the side of the leg you’re stretching as well as forward.
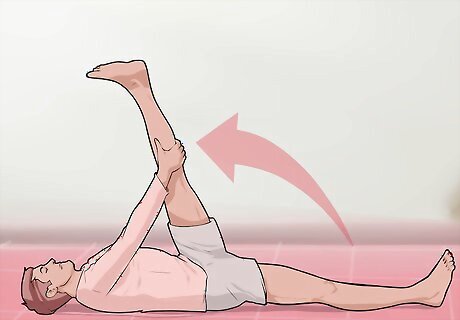
Do a lying hamstring stretch to maintain flexibility. Lie flat on your back, then bend your knee of the leg you want to stretch. Place one hand on the back of your thigh and the other on the back of your calf. Pull your leg toward you with your hands, keeping your knee bent around 20°. You’ll likely feel a stretch at the back of your thigh. Hold the position for 30 to 60 seconds. Repeat 3 times per session twice daily in addition to before and after exercising. If you can't reach your leg to pull it in, try placing a towel around your leg. You can then achieve the same stretch by pulling on the towel instead.
Perform seated hamstring stretches for flexibility. Sit down on the edge of a chair for this exercise. Bend your good leg in a normal sitting position, and place your injured leg in front of you with your knee bent only slightly. Lean forward from this position (keeping your back straight and head up) until you feel the stretch around the back of your thigh. Remain in this position for 30 seconds. Do 3 repetitions per session twice daily or before and after exercising.

Do knee bends to help with range of motion. While sitting, alternate between bending and straightening out your knee as far as you can without causing additional pain. This exercise will help you maintain your normal range of motion. Perform once a day with up to twenty repetitions if you feel no pain.
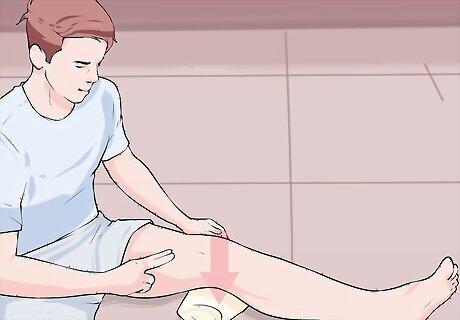
Do static quadriceps contractions for strengthening. Place a rolled towel under your knee with your leg out straight. Push your knee down against the towel to tighten your thigh muscles (quadriceps). Place your fingers on your quadriceps in order to feel the muscle tighten as you contract. Hold each repetition for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times as hard as possible without producing pain.

















Comments
0 comment