
views
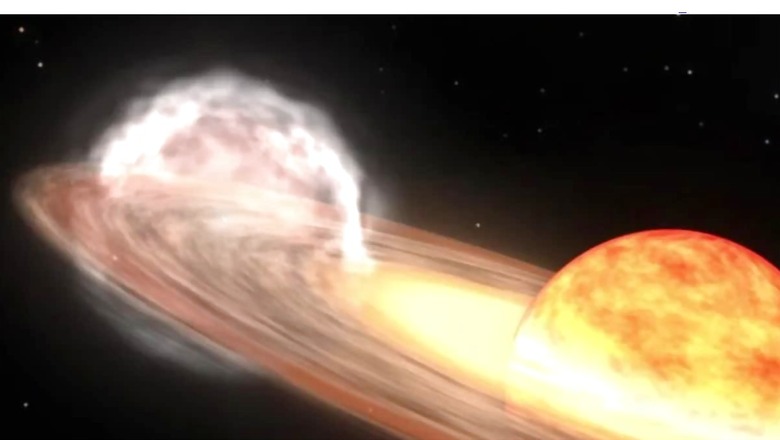
T Coronae Borealis also known as the Blaze Star is a binary star located 3,000 light-years from the Earth in the Corona Borealis constellations. This star has attracted much attention recently due to predictions of it exploding with nova, which can be viewed with the naked eye for the first time in nearly 80 years. The last recorded explosion was in 1946, and astronomers have observed the rise of T CrB’s activity since 2016.
The expected Nova explosion has not taken place by the first week of October 2024. As per the predictions made, it should have happened at any time between April of 2024 and September at the earliest, but T CrB still remains faint. Besides, there was a low-intensity event of the star in 2023, by which astronomers expect an explosion shortly. But with no activity until September, now experts are left just waiting for this kind of celestial event.
Under favourable conditions, T CrB has a visual magnitude of approximately +10 and, therefore, is essentially not visible to the bare eye. Nonetheless, during a nova event, it should shine at approximate magnitude +2 which is as bright as the Polaris, and visible with the naked human eye.
After the explosion of the star, astronomers forecast that it will remain visible for a week and then fade again. Onlookers are advised that the best vantage point will be approximately one day after the explosion. If one wants to find T Coronae Borealis in the night sky first, he or she needs to locate the Big Dipper’s handle and move towards the Arcturus star. From there, they can find Corona Borealis near it.
The Blaze Star has gone through an explosion about every 80 years. It has erupted twice before in 1866 and in 1946. The current cycle implies that we have reached the time of another eruption, however, there are theories of some astronomers that it can occur somewhat earlier because of patterns before the previous eruptions.
Though the exact timing is unknown, it is most likely to occur soon. Professor of Astrophysics and Planetary Science at Villanova University in Pennsylvania Edward Sion wrote an email to Forbes stating that “Each passing day in September, the probability of the outburst increases.” “It could explode at any time,” said Sion.
What is a Nova?
A nova is a discrete event in which a white dwarf star in a binary system acquires a material from its companion star which is generally a red giant. When this material accumulates, then a rise in pressure and temperature occurs until a thermonuclear event occurs on the surface of the visually impaired giant. This causes an immediate increase in brightness and that makes the Nova viewable from the Earth’s surface. After this, the star will take some time before it comes back to a normal level of brightness just like any other star.



















Comments
0 comment