
views
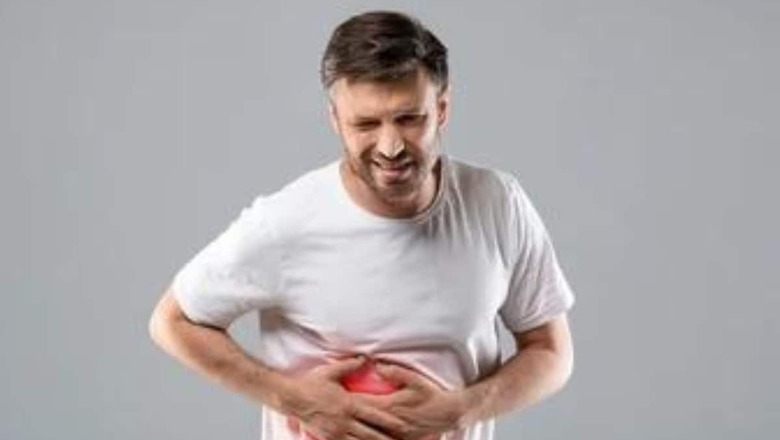
The liver is a vital organ that performs numerous crucial functions in the body, including detoxification, metabolism, and the production of essential proteins. However, certain disorders can impair normal functioning and lead to significant health complications. Three common liver disorders are hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease.
The inflammation of the liver known as hepatitis is frequently brought on by viral infections. The most common types of viral hepatitis are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and Hepatitis E. These viruses can be transmitted through contaminated food or water, sexual contact, or contact with infected blood. Hepatitis can also result from excessive alcohol consumption, autoimmune diseases, or certain medications and toxins. Symptoms of hepatitis include fatigue, jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Vaccinations are available for hepatitis A and B, and antiviral treatments can help manage hepatitis C.
Cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease characterized by progressive and irreversible scarring of liver tissue. Prolonged alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and autoimmune diseases are common causes of cirrhosis. As the liver becomes scarred, its ability to function properly is impaired, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal swelling, jaundice, fluid retention, and easy bruising and bleeding. Treatment for cirrhosis focuses on managing its underlying causes, preventing further liver damage, and addressing complications. A liver transplant may be required in extreme situations.
When fat builds up inside the liver cells, fatty liver disease develops. Alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are the two main varieties. AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, while NAFLD is associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD is becoming increasingly prevalent due to the rising rates of obesity and unhealthy lifestyles. Most individuals with fatty liver disease exhibit no symptoms, but as the condition progresses, it can lead to inflammation, liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and cancer of the liver. Treatment involves lifestyle changes such as weight loss, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing underlying conditions.
The prevention and management of these liver disorders primarily involve adopting healthy lifestyle habits. This includes practising safe sex, getting vaccinated against hepatitis, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding the use of illicit drugs. Regular medical check-ups are essential for early detection and intervention, as some liver disorders can be asymptomatic in the early stages.
In conclusion, hepatitis, cirrhosis, and fatty liver disease are common liver disorders that can have serious consequences if left untreated. Raising awareness about these conditions, promoting preventive measures, and ensuring early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial steps in safeguarding liver health. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical care, individuals can protect their liver and overall well-being.
















Comments
0 comment