
views
X
Trustworthy Source
PubMed Central
Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health
Go to source
This high-fat, low-carb diet causes you to go into ketosis, where your body starts torching fat for energy.[2]
X
Trustworthy Source
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School's Educational Site for the Public
Go to source
Some studies even show that a keto diet can help treat Alzeheimer’s, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s![3]
X
Trustworthy Source
PubMed Central
Journal archive from the U.S. National Institutes of Health
Go to source
Interested in trying this diet out for yourself? We’ve put together plenty of helpful tidbits and suggestions to help you get started.
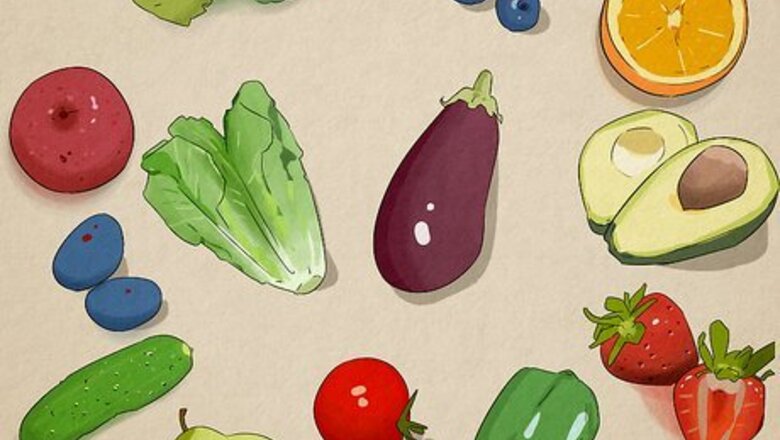
Munch on low-carb fruits and veggies.

On the keto diet, carbs should only be about 5-10% of your total calories. Thankfully, fresh produce isn’t blacklisted from the keto diet, and is a great way to meet your daily carb limit. Zucchini, cucumber, avocado, eggplant, tomato, lettuce, cauliflower, and broccoli are all excellent low-carb options to choose from. Fruits like raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, and strawberries are also low in carbs.
Transition into keto with a low-carb diet.
This can reduce some of the initial side-effects of starting keto, often called the keto flu. Symptoms of the keto flu include nausea, intestinal discomfort, or sleep issues. You can try the Atkins or the Paleo diets, since both are low-carb.
Stock up on healthy fats.
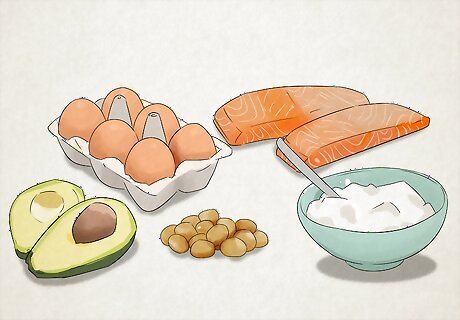
About 70-80% of your calories should come from fat. Cook your meals with olive and avocado oil, and snack on chia, sesame, and pumpkin seeds when you get hungry. Foods like full-fat Greek yogurt, macadamia nuts, salmon, tuna, avocados, eggs, coconut milk, coconut oil, and grass-fed steak are other great sources of fat. Cheese and heavy creams are also rich in fat. For example, if you’re following a 2,000 calorie diet, you might eat about 165 grams of fat each day.
Eat plenty of proteins.
You’ll get around 10-20% of your calories from protein. Chow down on venison, beef, dark chicken meat, dark turkey meat, lamb, and pork. If you’re a seafood fan, you’re in luck—salmon, tuna, and shrimp are also excellent protein sources. Stock up on plenty of dairy products too, like whole milk cottage and ricotta cheese, along with Greek yogurt. In a 2,000 calorie diet, you might eat about 75 grams of protein every day.
Supplement your diet with short-chain fats.

Short-chain fats instruct the liver to make more ketones. These can ease the process of ketosis and reduce stress on your body. Coconut oil is a good source of short-chain fats.
Take a vitamin D supplement.

Vitamin D is essential to calcium consumption, cell growth, and inflammation. Unfortunately, this nutrient is rarely naturally present in foods. Stop by your local health food store and pick up some vitamin D capsules or pills to help balance out your diet. You can also get vitamin D sun exposure. Try to sit outside or go for a walk each day.
Choose a targeted keto diet if you’re a frequent exerciser.
This ensures you’ll have enough energy to work out. Generally, targeted keto diets (TKD) are 65-70% fat, 20% protein, and 10-15% carbs. The carbs will be most helpful if eaten before or after you work out. These carbs will be burned as you exercise, and therefore won’t get stored as fat.
Pick a cyclical keto diet for more freedom on cheat days.

Save those cheat days for special occasions. Or, you might alternate five days of a normal keto diet with two non-keto days. For example, a “keto day” could have 75% fat, 15-20% protein, 5-10% carbs, while an “off day” could have 25% fat, 25% protein, 50% carbs. Even on your off days, try eating fruits, starchy veggies, dairy, and whole grains for your carbs instead of sugary or highly processed foods.
Try a high-protein keto diet to build muscle.
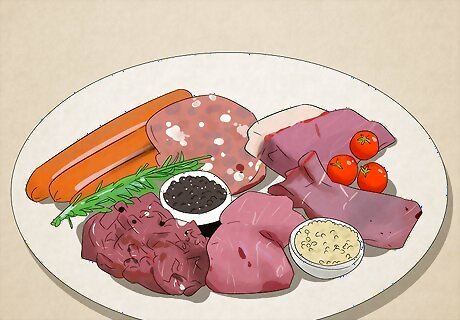
If you lift weights 4-6 times a week, this is a good option for you. For reference, a high-protein keto diet is around 60% fat, 35% protein, and 5% carbs. This diet is easier to follow because you replace some of the fat from the standard keto diet with protein. If you are using a ketogenic diet to lose weight or build muscle mass, eat approximately 1g of protein per pound of body mass.
Test for signs of ketosis.
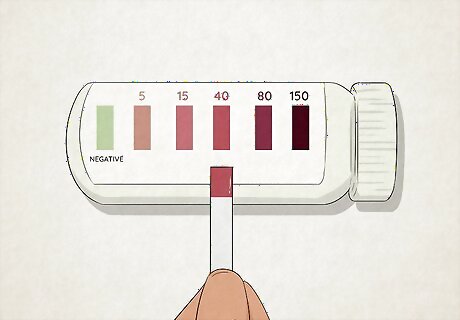
This is a surefire way to know if your ketogenic diet is effective. To know for sure, use ketosis test stips to see how many ketones are in your urine. You could also try a breathalyzer test, which checks for acetone in your breath. For really accurate results, ask your doctor to test your blood for serum blood ketones, or invest in a blood glucose meter that tests for ketones. When you’re in ketosis, you might have bad breath, low energy, flu-like symptoms, constipation, and frequent urges to use the restroom. It will usually take about 3 days to get into ketosis, though this number can differ depending on how old you are, the speed of your metabolism, and how much you’re limiting your carb intake.
Consult your physician before starting a keto diet.

They can help you make sure you’re pursuing ketosis healthily. Also, discuss the possibility of potential complications if you have preexisting health conditions or metabolic disorders. Ask your doctor if a ketogenic diet might help treat existing health conditions or preemptively treat conditions you might be prone to, like diabetes. Check with your physician or doctor to see if you are at risk for ketoacidosis.














Comments
0 comment