views
Easing Nighttime Tooth Pain
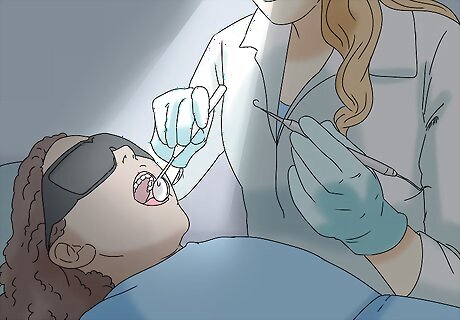
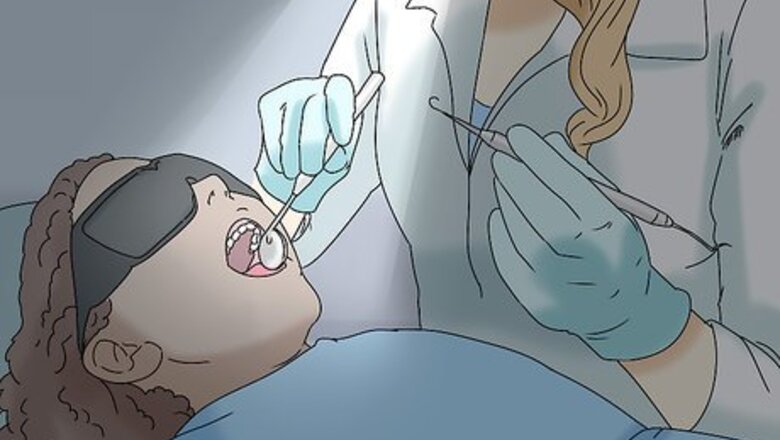
See your dentist to treat the cause of your tooth pain. If you have a toothache, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible to figure out what’s causing the problem. They may give you a dental exam and take x-rays to find the source of your pain. Once they diagnose the issue, they can begin treatment and offer advice to help you manage any nighttime pain. Common causes of toothache include tooth decay, dental abscesses, cracked teeth, loose fillings, gum infections, and problems with braces. Call your dentist immediately if your toothache that lasts longer than 2 days or if it is accompanied by symptoms such as fever, redness and swelling of the gums, discharge that smells or tastes bad, difficulty breathing or swallowing, or pain when you bite down.

Use an over-the-counter medication to reduce pain and swelling. Before bed, take a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), such as ibuprofen (Motrin or Advil) or naproxen (Aleve). These can help bring down inflammation and soothe your pain. Follow the dosage directions on the package or get advice from your doctor or dentist. Don’t use NSAIDs if you are pregnant or if you have a bleeding disorder. Talk to your doctor or dentist if you have any health concerns, and let them know if you are currently taking any other medications. If your dental pain is severe, talk to your doctor or dentist about using NSAIDs together with acetaminophen (Tylenol) for more effective pain relief. Don’t use aspirin if you are younger than 18 or if you are experiencing any bleeding from your mouth or gums. Because of potentially severe side effects, many dentists no longer recommend using topical benzocaine products (such as Anbesol or Orajel) to treat toothaches. Never give any medication containing benzocaine to a child under 2 years old.
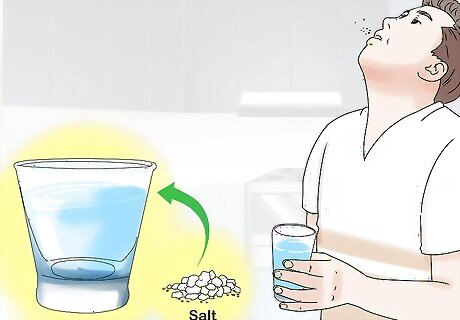
Rinse your mouth with saltwater before bed. A warm saltwater rinse can soothe your pain and kill bacteria that might be contributing to your toothache. Rinse your mouth with saltwater at least 2-3 times per day while you have your toothache, and make sure to do one of these rinses right before bedtime.To make a saltwater rinse: Stir 1 teaspoon (6 g) of salt into about 100 millilitres (0.42 c) of warm water until the salt is completely dissolved. Swish the saltwater solution in your mouth for at least 1 minute, focusing your attention on the painful area. Spit out the solution when you are done. Some dentists recommend swishing ice water instead, since the cold can soothe your pain and reduce inflammation.

Use an ice pack on your jaw before you sleep. If your toothache is accompanied by tenderness and inflammation, an ice pack can help bring down the swelling and prevent fluids from building up in the area. Take an ice pack or a package of frozen peas and wrap it in a towel. Apply the ice pack to the painful or swollen area for 10 minutes at a time, once an hour, in the last few hours before bed. Always keep a thin layer of cloth between the ice and your skin to avoid ice burns. Avoid using a heat source, such as a warm compress, to soothe your aching jaw. Heat may make your inflammation worse.
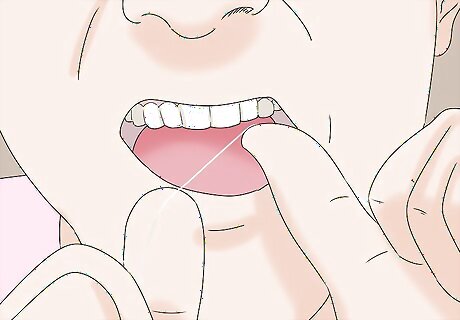
Floss between the affected teeth at bedtime. Before you go to sleep, floss your teeth, focusing on the area where the pain is located. Removing built-up particles between your teeth can help relieve pressure that may be contributing to the toothache. Carefully guide the floss around the contours of your teeth. Work the floss between your teeth using a rocking or sawing motion so that it does not snap up abruptly and damage your gums.

Sleep with your head elevated. When you’re ready to go to bed, prop your head up on 1 or more pillows. If you use just 1 pillow, make sure it’s thick enough to elevate your head and shoulders. Elevating your head can minimize inflammation by preventing fluids from building up around the troublesome tooth. If possible, try to sleep sitting up slightly (e.g., in a recliner or propped up on a bed lounger).
Taking Preventative Measures

Minimize your sugar intake. Eating too much sugar can contribute to dental decay and make existing toothaches worse. Avoid sugary foods, such as candy, sweet baked goods, ice cream, and soda. Acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits, fruit juices, and carbonated beverages, can also irritate your teeth and cause decay.
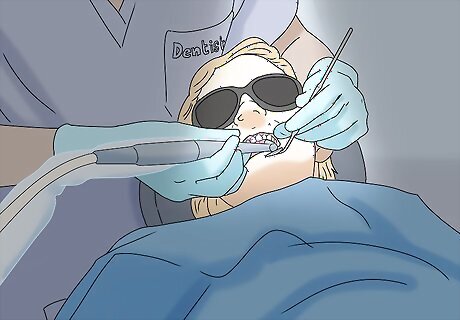
See your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. Regular dental checkups and hygiene visits are critical to preventing tooth decay, damage, and pain. See your dentist for a cleaning and checkup once or twice a year, or as often as they recommend based on your dental health. In addition to doing a visual exam and cleaning, your dentist may wish to take X-rays to spot cavities and other problems that aren’t easy to see with the naked eye.
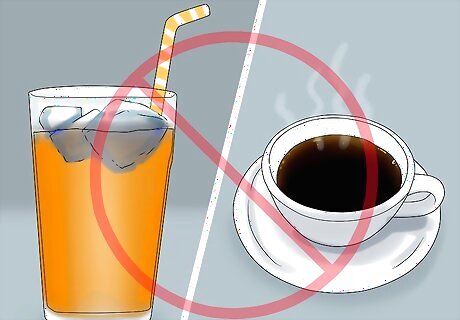
Avoid eating foods that are very hot or very cold. If you’re already dealing with dental pain, extreme temperatures can make it worse. Avoid cold foods and drinks (such as ice cream, popsicles, smoothies, and icy drinks) as well as very hot ones (like hot coffee, tea, or soup). If you experience tooth pain that lasts for more than 30 seconds after eating hot or cold foods, see your dentist right away. This may be a sign that the pulp of your tooth is exposed or damaged. If your teeth are sensitive to hot or cold, try using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth. Brush your teeth with a soft-bristle brush, and make sure to use an up-and-down rather than side-to-side brushing motion to avoid damaging exposed roots.
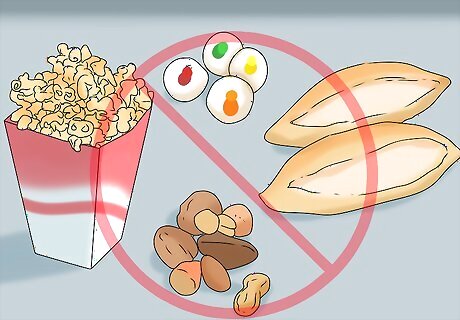
Stay away from extremely hard or crunchy foods. Some hard foods—such as hard candies, nuts, popcorn kernels, or hard bread rolls—can crack your teeth or chip your enamel, contributing to dental pain and making you more prone to infections. Hard foods can be extra hazardous if your enamel is already cracked or thinning. Hard candies are especially dangerous to your teeth—not only can they chip your enamel, but the chewed-up candy can cling to your teeth and contribute to decay.
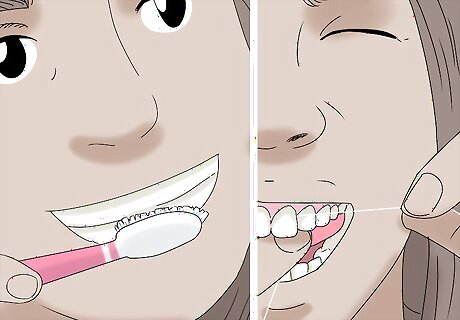
Brush and floss your teeth regularly. Good dental care is a critical part of preventing and managing tooth pain. Even if you’re already dealing with a toothache, continue to brush your teeth twice a day and floss at least once a day. Keeping your teeth clean will help prevent further decay, inflammation, and damage that could make your dental pain worse.
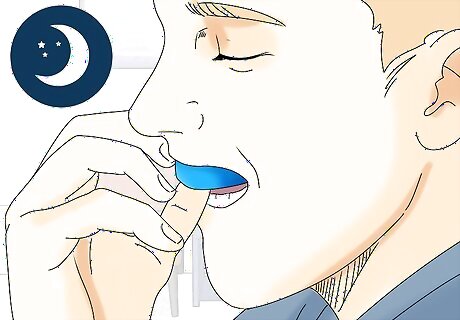
Wear a mouth guard at night if your dentist recommends it. You might experience tooth pain or damage to your teeth if you clench or grind your teeth at night. At your next dental checkup, ask your dentist to examine you for signs of bruxism (teeth grinding). They may recommend using a splint or dental guard to protect your teeth while you sleep. Other treatments for bruxism include: Dental corrections (such as caps or crowns) to fix teeth that have been damaged by grinding. Stress relief techniques to minimize tension that may be contributing to your tooth grinding behaviors. Medications to relax the muscles in your jaw or to relieve symptoms of stress and anxiety.




















Comments
0 comment