
views
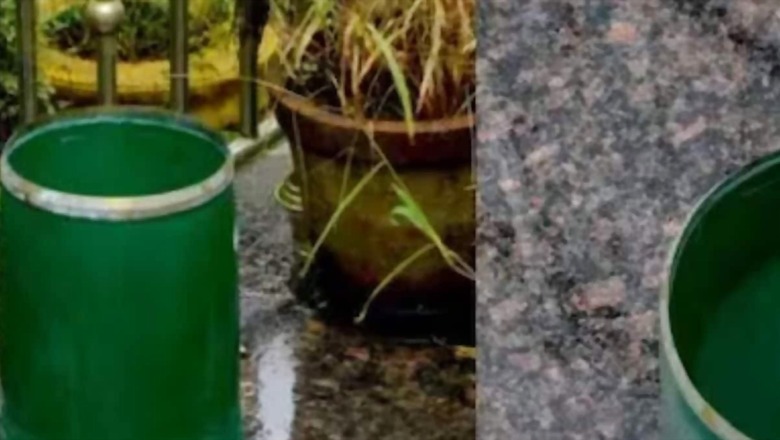
In Kerala’s Wayanad, the District Disaster Management Authority collects rainfall data through rain gauges. More than 200 rain gauges have been installed at various places, including the Collectorate. A rain gauge is a device used to measure the amount of rain received in an area within a given period of time. The main parts of a rain gauge are a funnel with a fixed mouth and a cylinder attached to collect rainwater. The height from the bottom to the top of one side of the vessel shall be marked in mm. It is possible to observe the variation of rainfall according to the different topographies of the district and identify the microclimate characteristics through rain gauge observation. This system can calculate the amount of rainfall recorded in each area and issue warnings. A website and app called DM Suite has been prepared in the district to record the information received from rain gauges. According to reports, this is India’s first rain gauge website.
The information obtained from the rain gauges is available through the app, so it is possible to adjust the rain map quickly. Red, orange, and yellow alerts can be announced in the area, and preparations can be made by calculating the amount of rain received in each land area.
Monitoring is done through rain gauges in high-altitude areas like Meppadi, Brahmagiri, Kambamalla, Makhimala, Banasura, Siddhagiri, Lakithi, Mullankolli, and Pulpally, which receive less rainfall. An area receiving continuous rainfall of more than 600 mm is considered vulnerable to landslides and floods.
Rain gauges can be used to detect and prevent disasters such as landslides and mountain floods. Disaster Management Authority Chairperson, DR District Collector D.R. Rangashree said that by understanding natural calamities in advance, necessary precautions can be taken. With such a project, rain gauges in Wayanad are not just rain gauges but also a new idea in local weather monitoring.



















Comments
0 comment